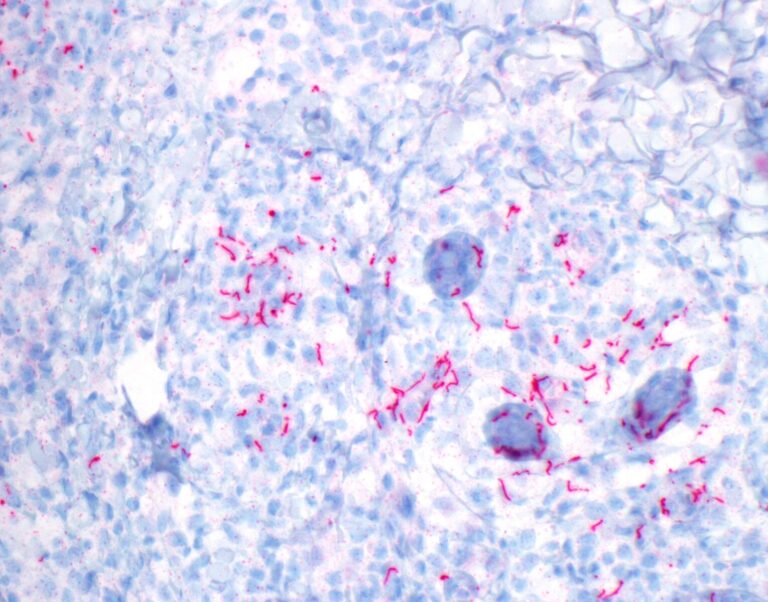
Scientists have used genomics to disclose distinct sexual networks for syphilis transmission, outlined geographically or by sexual choice, amongst a background of wider circulation in England. Additionally they present a presence of drug resistance within the majority of instances.
By grouping intently associated strains of the bacterium that causes syphilis—Treponema pallidum—researchers reveal how a lot of instances are linked collectively.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and their collaborators on the UK Well being Safety Company (UKHSA) sequenced 237 complete genome samples and built-in this with epidemiological information to map the bacterium’s evolution and unfold via a inhabitants. They present distinct transmission chains between people in addition to vital resistance to a generally prescribed class of antibiotics in England.
The findings, revealed in The Lancet Microbe, assist reveal the utility of genomics to grasp syphilis transmission patterns, revealing data past what customary epidemiological surveillance information can present.
Unpacking STI developments utilizing genomic surveillance may assist determine high-risk areas or populations and inform focused public well being methods to interrupt the chains of transmission. The findings warrant additional investigation into the function of genomics throughout completely different settings and STI-causing micro organism.
Instances of syphilis have tripled up to now decade in England, growing from 2,648 diagnoses in 2010 to 7,982 in 2019. The will increase are regarded as partially fostered via overlapping sexual networks of homosexual, bisexual and different males who’ve intercourse with males (GBMSM) in addition to ladies. Whereas routine epidemiological information present insights into the present rise in syphilis charges, it struggles to indicate how the bacterium circulates inside a inhabitants at nationwide and regional ranges.
For instance, a gaggle of clustered syphilis instances—shut in time and proximity—may signify a single outbreak and chain of transmission, however is also the results of separate co-circulating networks.
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted an infection brought on by the bacterium, Treponema pallidum (T. pallidum). Whereas the genomes of T. pallidum are extremely conserved in comparison with different bacterial pathogens—as they have an inclination to transmit extra steadily than they mutate—refined variations can nonetheless exist because it spreads via a inhabitants. By evaluating how genetically associated T. pallidum samples are between people with a syphilis analysis, scientists hope to pinpoint the supply of syphilis outbreaks and assemble networks that seize its unfold.
On this new research, researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and their collaborators got down to check the usage of genomic surveillance to resolve native transmission chains for T. pallidum and higher perceive the genomic panorama for syphilis in England.
The crew mixed anonymized affected person demographic and epidemiological information with complete genome sequencing evaluation of T. pallidum genomes from 237 sufferers identified with syphilis in England between 2012 and 2018. By evaluating the bacterial genomes from completely different people, researchers have been capable of determine single letter adjustments within the DNA—referred to as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)—to differentiate one pressure, or sublineage of T. pallidum from one other.
Researchers recognized a number of options of transmission networks of T. pallidum in England, affecting GBMSM and heterosexuals at nationwide and regional ranges. They have been capable of make inferences of latest transmission primarily based on how associated—similar or extremely comparable—T. pallidum genomes have been throughout completely different people. These inferences have been later verified by epidemiological information.
Whereas earlier work has grouped T. pallidum lineages separated by a few years with a lot of SNPs, the brand new research goes all the way down to the similar gene stage with zero SNPs, indicating latest transmission. This never-seen-before decision may enable public well being authorities to map syphilis unfold in an ongoing outbreak.
The researchers’ evaluation of T. pallidum genetic range additionally highlights the extent of drug resistance in England. Lots of the 237 genome samples sequenced have been immune to macrolides, a category of antibiotics generally used to deal with many STIs. The work subsequently aids in public well being coverage round safeguarding ineffective use of antibiotics as a part of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) stewardship efforts and informs greatest therapies for sufferers.
Dr. Mathew Beale, first creator of the research and senior employees scientist on the Wellcome Sanger Institute, stated, “The COVID-19 pandemic has reimagined what scale is feasible in genomic surveillance and this research capitalizes on that, offering necessary background data on how briskly the genomes of T. pallidum evolve as syphilis spreads via a inhabitants.”
“We should always discover with future sampling work whether or not these evolutionary baselines are consultant and if the strategy can be utilized robustly in settings outdoors of England. Syphilis genome range is poorly understood in international locations the place STI management applications are most wanted.”
Dr. Helen Fifer, senior creator and lead microbiologist for bacterial sexually transmitted infections on the UK Well being Safety Company, stated, “We’re seeing document ranges of STIs together with syphilis.”
“Genomics supplies yet one more software in our toolbox for understanding chains of transmission of syphilis and predicting response to therapies. We should additionally give attention to available prevention methods and STI companies, resembling condoms, together with details about their limitations, efficient follow-up of individuals with new STI diagnoses and self-monitoring for signs when crucial.”
Professor Nicholas Thomson, senior creator and program chief from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and the London College of Hygiene & Tropical Medication, stated, “In some ways, syphilis is difficult to trace with genomic surveillance given how slowly it mutates. The truth that we’ve got demonstrated the usefulness of analyzing each completely different and similar bacterial genomes to assist make inferences about sexual transmission is thrilling.”
“In different STIs resembling gonorrhea, chlamydia and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) we might be able to cluster strains into direct transmission occasions, confirming patient-patient contact. Whereas its use will should be investigated additional, genomic surveillance may present a step change in our capability to grasp and inform surveillance, prevention, and remedy methods for a broad vary of STIs.”
Dr. Ana Cehovin, Senior Analysis Supervisor, Infectious Illness at Wellcome, stated, “Genomic surveillance is a useful software for understanding how illnesses are spreading, what populations are at elevated danger and which strains are growing drug resistance. Utilizing this data, we are able to spot outbreaks or incidences of drug resistance earlier, and subsequently take motion to guard at-risk communities.”
“This research exhibits the significance of constructing trusted relationships and shut collaboration between researchers and public well being companies, to allow a fast response to adjustments in illness transmission and unfold and goal interventions and coverings extra successfully. Equally, realizing the potential of genomic surveillance to determine and monitor drug resistance might help determination makers to implement crucial mitigation measures to regulate the unfold of resistant strains, lowering the prospect of illness escalation and defending at-risk communities.”
Extra data:
M. A. Beale et al, Genomic epidemiology of syphilis in England: a population-based research, The Lancet Microbe (2023). DOI: 10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00154-4. www.thelancet.com/journals/lan … (23)00154-4/fulltext
Quotation:
Syphilis transmission networks and antimicrobial resistance in England uncovered utilizing genomics (2023, September 15)
retrieved 15 September 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-09-syphilis-transmission-networks-antimicrobial-resistance.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.