In a current assessment article revealed within the journal Antioxidants, researchers explored how environmental components influence the mind improvement of fetuses and neonates, emphasizing irritation and oxidation stress as frequent denominators throughout numerous stressors.
Their conclusions spotlight the crucial function of wholesome intrauterine environments for selling fetal mind improvement and stress the significance of interventions that purpose to cut back modifiable stress components throughout being pregnant.
 Assessment: Influence of Maternal Setting and Irritation on Fetal Neurodevelopment. Picture Credit score: Sebastian Kaulitzki / Shutterstock
Assessment: Influence of Maternal Setting and Irritation on Fetal Neurodevelopment. Picture Credit score: Sebastian Kaulitzki / Shutterstock
Background
The event of the human mind, which commences through the second to 3rd week of gestation and continues by childhood, is influenced by a mixture of genetic, epigenetic, and environmental components.
Key developmental milestones happen throughout particular gestational intervals, reminiscent of mobile migration within the neocortex and in depth neurogenesis between the eighth and eighteenth weeks.
Maternal environmental exposures through the prenatal and antenatal intervals can influence intrauterine improvement and the quick—and long-term well being of the offspring, doubtlessly elevating the dangers of creating non-communicable illnesses in maturity.
These exposures can epigenetically modify placental and fetal phenotypes, affecting organ construction, metabolism, and physiology. Nonetheless, understanding the exact molecular mechanisms linking exterior components to neurodevelopmental alterations stays difficult.
On this assessment, researchers aimed to discover the results of assorted maternal environmental exposures, together with vitamin, way of life, stress, and air pollution, on fetal mind improvement and neonatal neurodevelopment-related outcomes, drawing from a complete literature search that encompassed human and animal research revealed throughout the final 15 years.
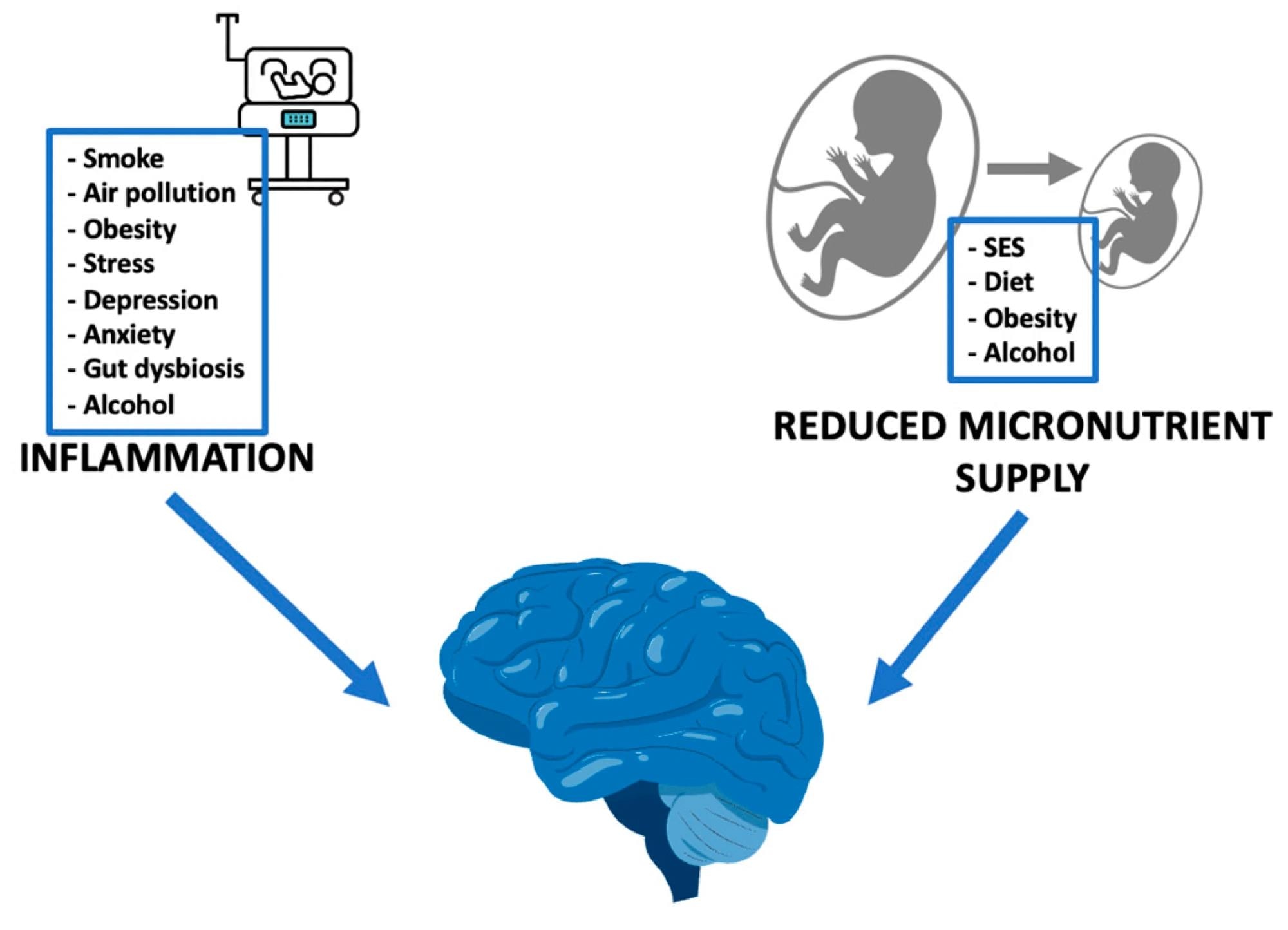 Exterior stimuli, by irritation and decreased micronutrient provide, influence on fetal neurodevelopment. SES: socioeconomic standing.
Exterior stimuli, by irritation and decreased micronutrient provide, influence on fetal neurodevelopment. SES: socioeconomic standing.
Maternal environmental exposures
Maternal vitamin performs a vital function in fetal neurodevelopment, with proof suggesting that each inadequate and unhealthy dietary patterns throughout being pregnant can have an effect on fetal mind improvement.
For instance, the Mediterranean weight loss program, characterised by nutrient-rich meals, has been related to optimistic neurodevelopmental outcomes in offspring.
Nonetheless, deficiencies in micronutrients like docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), folate, and iodine and extreme consumption of macronutrients have been linked to adversarial neurodevelopmental results.
The Western weight loss program, specifically, is thought to be excessive in macronutrients however poor in micronutrients. Inexpensive however low-quality meals characterize it. Mouse fashions recommend that pow-protein diets may be related to neurodevelopmental delays.
Alterations in maternal intestine microbiota throughout being pregnant have been linked to worse behavioral outcomes in offspring, doubtlessly mediated by irritation and metabolic endotoxemia.
Maternal weight problems and a high-fat weight loss program have additionally been implicated, with animal fashions and epidemiological research suggesting associations with cognitive deficits, consideration deficit hyperactivity dysfunction (ADHD), autism, and psychoses in offspring.
Moreover, maternal melancholy, anxiousness, and stress can result in disturbed fetal neurodevelopment, doubtlessly leading to altered mind construction and performance, as evidenced by investigations utilizing human and animal fashions.
Smoking and alcohol consumption throughout being pregnant have well-documented detrimental results on fetal neurodevelopment, together with elevated dangers of ADHD, autism, schizophrenia, and behavioral points.
Publicity to air air pollution, primarily particulate matter, and polycyclic fragrant hydrocarbons, has been linked to neurodevelopmental issues in offspring, with oxidative stress and inflammatory responses implicated as underlying mechanisms.
Socioeconomic standing additionally performs a task, with deprived circumstances related to adversarial being pregnant outcomes and poorer neurodevelopmental outcomes in youngsters.
Underlying mechanisms
Quite a few research have linked pathological being pregnant circumstances like fetal progress restriction (FGR) and preterm start (PTB) with neurodevelopmental points in offspring. Two principal mechanisms are implicated: altered fetal nutrient provide and intrauterine irritation involving placental components.
FGR, usually because of placental dysfunction, results in persistent fetal hypoxia and undernutrition, impacting fetal mind improvement regardless of adaptive responses like mind sparing.
PTB, usually linked to maternal irritation or an infection, presents numerous neurodevelopmental challenges, together with disruptions in axonal and neuronal improvement and mind abnormalities like cerebral palsy.
Irritation throughout being pregnant, exacerbated by components like weight problems, stress, and environmental pollution, influences insulin and neurotransmitter signaling, affecting synaptic plasticity and neurotrophic issue expression.
The activation of maternal immune techniques contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, perpetuating a cycle of oxidative stress and irritation that disrupts fetal mind improvement.
These circumstances and publicity to chemical substances can compromise the blood-brain barrier and result in extra impairments in fetal mind improvement.
General, maternal well being circumstances and exterior components collectively contribute to elevated maternal irritation, which impacts fetal neurodevelopment and doubtlessly results in long-term neurological penalties in offspring.
Conclusions
The assessment emphasizes how exterior components throughout being pregnant have an effect on fetal progress and mind improvement, impacting long-term neurodevelopment.
Circumstances like PTB and FGR alter mind morphometry, usually because of irritation and adjustments in nutrient provide. Proof suggests they’re influenced by maternal well being and environmental components like air air pollution and stress.
Understanding and addressing these modifiable threat components is essential for bettering each particular person and public well being outcomes. This highlights the significance of preventive measures and additional longitudinal analysis.
Journal reference:
- Impacts of maternal setting and irritation on fetal neurodevelopment. Lubrano, C., Parisi, F., Cetin, I. Antioxidants (2024). DOI: 10.3390/antiox13040453, https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3921/13/4/453

