A staff of scientists, led by Duke-NUS Medical Faculty, has found a possible intranasal vaccine candidate that gives improved, longer-lasting immunity towards SARS-CoV-2 viruses in comparison with when given as an injection. By triggering an immune response straight on the level of entry, the intranasal vaccine candidate enhanced long-term immune reminiscence of the virus, which might translate to a lowered want for booster pictures.
There may be rising proof that intranasal vaccines present larger safety at mucosal surfaces, making this a vaccination route that might scale back breakthrough infections and subsequent transmission of the virus.
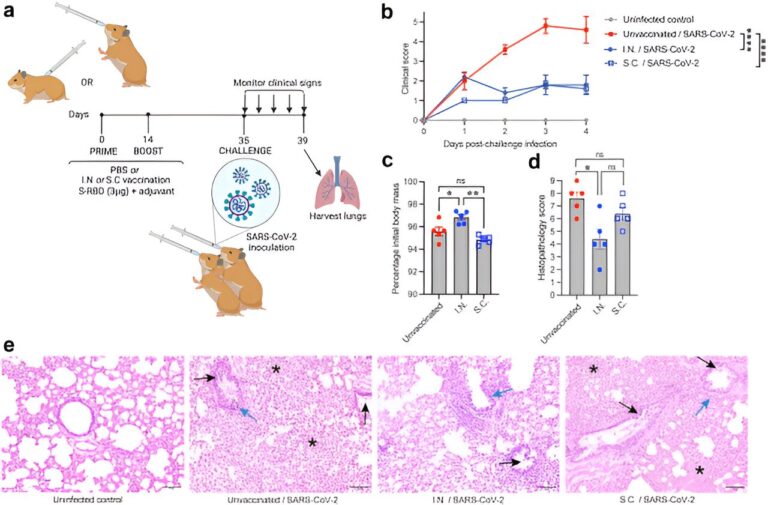
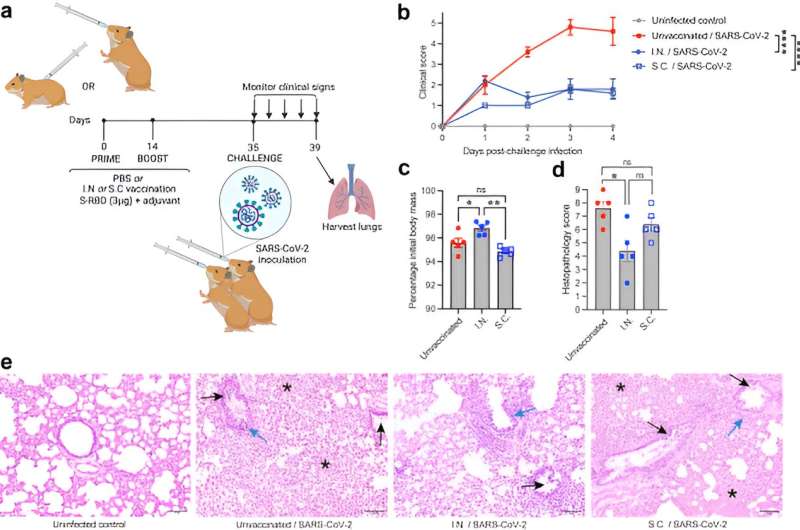
To delve into this, the analysis staff, which incorporates collaborators from Duke-NUS’ dad or mum universities—Duke College and the Nationwide College of Singapore—amongst others, in contrast the immune responses from nasal and subcutaneous administration of the vaccine, in addition to immunity from the vaccine with and with out using adjuvants—substances added to vaccines to reinforce the physique’s immune response.
Revealed in eBioMedicine, the findings confirmed nasal administration of the vaccine candidate boosted mucosal antibody response, as anticipated. Moreover, and extra importantly, it enhanced longer-lasting mucosal and systemic immune safety by way of preferential induction of airway-resident T cells and central reminiscence T cells.
“Our information present that, in comparison with subcutaneous vaccination, the intranasal route improved the response of sure immune cells, often called T cells, which lowered illness severity,” defined Affiliate Professor Ashley St John, from Duke-NUS’ Rising Infectious Illnesses Program, who’s the lead writer of the research.
“Not solely that, but it surely additionally resulted in a larger variety of T central reminiscence cells in comparison with subcutaneous vaccination, which might result in longer-lasting safety.”
T central reminiscence cells play a significant function in safeguarding the physique upon re-exposure to a virus. They improve the immune system’s reminiscence, inducing long-lasting protecting immune responses. This capability to retain this long-term reminiscence of the virus suggests much less want for a pathogen problem to realize the identical stage of safety towards the virus, doubtlessly translating into fewer boosters.
The analysis staff additionally discovered that using adjuvants within the vaccine to advertise immune response influenced the traits of T cells, in addition to their activation and manufacturing of cytokines—tiny proteins that regulate cell communication and management irritation—with completely different adjuvants resulting in completely different T-cell responses.
One other notable discovering from the research was {that a} kind of antibody, referred to as IgG, that circulates extensively within the bloodstream is more practical at neutralizing variants of the virus, together with newly emergent ones, when induced by way of the nasal vaccine route. These discoveries present vital scientific proof that improved immunity responses from each T cells and IgG antibodies contribute to larger and long-lasting safety of intranasal vaccines from COVID-19.
“Whereas the acute part of the pandemic could also be behind us, the rise of latest variants, together with JN.1, which has triggered a rise in hospital admissions regionally, demonstrates that we’ve got room in our arsenal of vaccines and coverings for even higher instruments. This research exhibits that mucosal vaccination holds promise for enhancing COVID-19 vaccine efficacy with doubtlessly fewer boosters wanted,” stated Professor Patrick Tan, Senior Vice-Dean for Analysis at Duke-NUS.
A patent has been filed on the invention, which covers the invention of the vaccine composition formulated for mucosal supply, paving the best way for an trade partnership to doubtlessly develop mucosal vaccines towards COVID-19 and different pathogens that additionally goal mucosal surfaces.
Extra data:
O’Neill A, Mantri CK, Tan CW, Saron WA, Nagaraj SK, Kala MP, Pleasure CM, Rathore APS, Tripathi S, Wang L-F, St. John AL. Mucosal SARS-CoV-2 vaccination of rodents elicits superior systemic T central reminiscence operate and cross-neutralising antibodies towards variants of concern. eBioMedicine (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104924.
Quotation:
Scientists uncover potential nasal COVID-19 vaccine candidate that gives higher and longer safety (2024, January 9)
retrieved 9 January 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-01-scientists-potential-nasal-covid-vaccine.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.