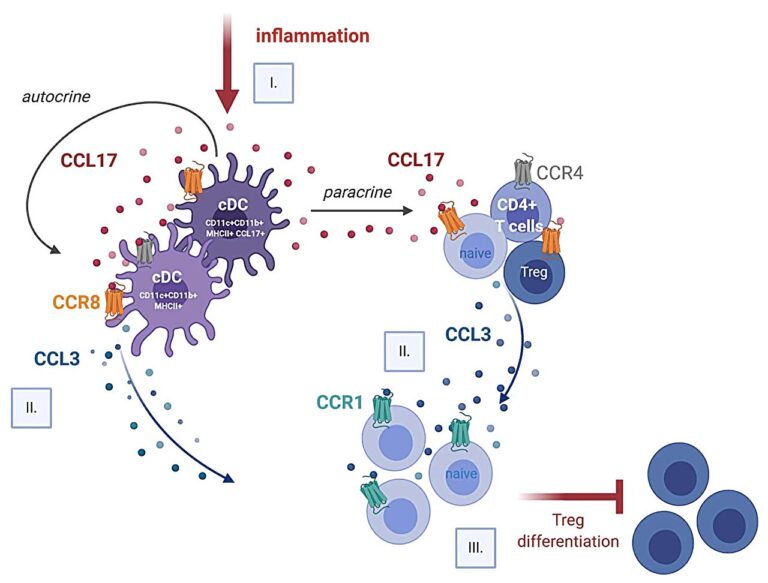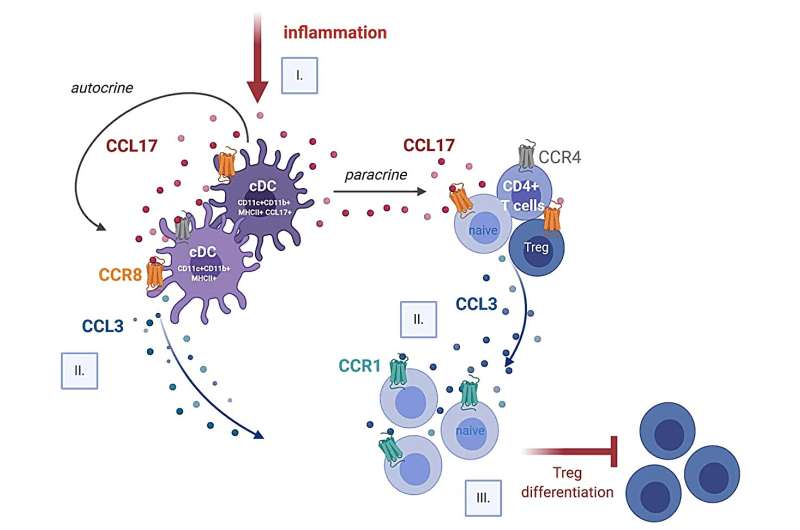
Atherosclerosis, a power inflammatory illness of the internal partitions of blood vessels, is chargeable for many cardiovascular situations. Dendritic cells, which act to acknowledge overseas substances within the physique and mount an immune response, play an essential position within the illness. They produce the signaling protein CCL17, a chemokine, which influences the exercise and mobility of T cells, which monitor down contaminated cells within the physique and assault the pathogens. Nevertheless, CCL17 may also promote cardiovascular pathologies.
Individuals who undergo from cardiovascular illnesses, or are explicit inclined to such illnesses, have elevated ranges of the signaling protein. In people and mice, elevated CCL17 serum ranges are related to elevated threat of atherosclerosis and inflammatory illnesses of the cardiovascular and digestive programs.
Nevertheless, scientists haven’t but managed to ascertain how precisely CCL17 produced by the dendritic cells regulates the T cells.
A staff led by LMU researchers Christian Weber and Yvonne Döring has demonstrated new mechanisms which can be concerned within the improvement of inflammatory cardiovascular illnesses. Their research has simply been revealed within the journal Nature Cardiovascular Analysis.
“We all know from our earlier work {that a} genetic deficiency or an antibody blockade of CCL17 impedes the progress of atherosclerosis,” says Weber, Director of the Institute for Cardiovascular Prevention at College of Munich Hospital and one of many lead authors of the brand new paper.
Prior to now, just one sign receptor was identified to contribute to the recruitment and capabilities of T cells. If this receptor is missing, nevertheless, the physique will not be shielded from the destructive results of CCL17, as Weber’s staff was in a position to show in a mouse research.
Mice that didn’t possess the receptor in query continued to have the identical extent of illness pushed by CCL17. If the signaling protein acted straight and solely on this receptor, then silencing it ought to have the identical results because the absence of CCL17.
Consequently, there have to be one other signaling pathway through which CCL17 is concerned, and the researchers demonstrated and described simply such a pathway in the midst of the brand new research. “We furnish clear proof that CCL17 acts via an alternate receptor with excessive affinity, thereby triggering a signaling pathway that ends in the suppression of anti-inflammatory, so-called regulatory T cells,” explains Weber’s colleague and first creator Döring.
These T cells would then not be capable of sort out the vascular inflammations. By concentrating on and inhibiting particular person receptors of the investigated signaling pathway in the midst of their experiments, the authors had been in a position to present that this mechanism performs a decisive position within the destructive results of CCL17.
Weber is satisfied that this accomplishes a serious step ahead within the understanding of inflammatory illnesses. “The response pathway we recognized represents a extremely related mechanism in power inflammatory illnesses and might be an essential place to begin for all kinds of therapeutic interventions.”
Extra info:
Yvonne Döring et al, Identification of a non-canonical chemokine-receptor pathway suppressing regulatory T cells to drive atherosclerosis, Nature Cardiovascular Analysis (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s44161-023-00413-9
Quotation:
Researchers uncover new signaling pathway within the improvement of atherosclerosis (2024, January 24)
retrieved 24 January 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-01-uncover-pathway-atherosclerosis.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.