A brand new examine from the College of Pittsburgh Middle for Vaccine Analysis printed as we speak within the Journal of Experimental Drugs describes a beforehand unappreciated position for a category of immune cells within the early phases of tuberculosis (TB) an infection.
The researchers discovered that innate CD8+ lymphocytes – a subtype of white blood cells concerned in speedy immune response – are important for curbing the illness. In addition they found that an inflammatory molecule known as Interleukin-15, or IL-15, performs an vital position in an infection management and will probably be used to spice up the efficacy of present and future TB vaccines.
That is an uncommon discovering. Nobody earlier than us has proven that CD8+ lymphocytes make a distinction early within the an infection in a translatable non-human primate mannequin, however our findings counsel that these innate immune cell populations are literally enjoying an vital position in restraining the preliminary an infection.”
JoAnne Flynn, Ph.D., senior creator, distinguished professor and chair of microbiology and molecular genetics at Pitt
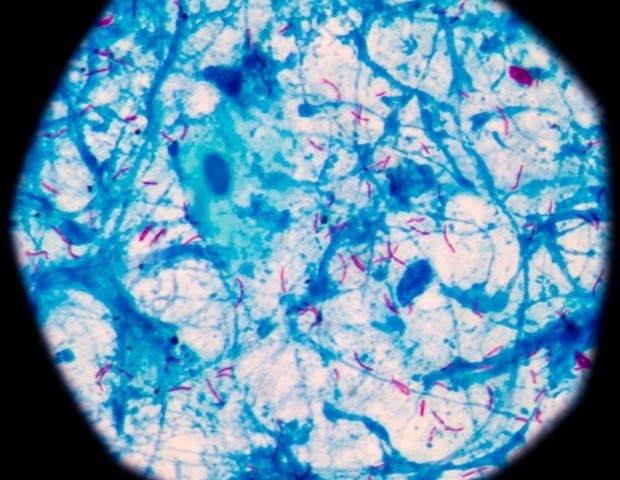
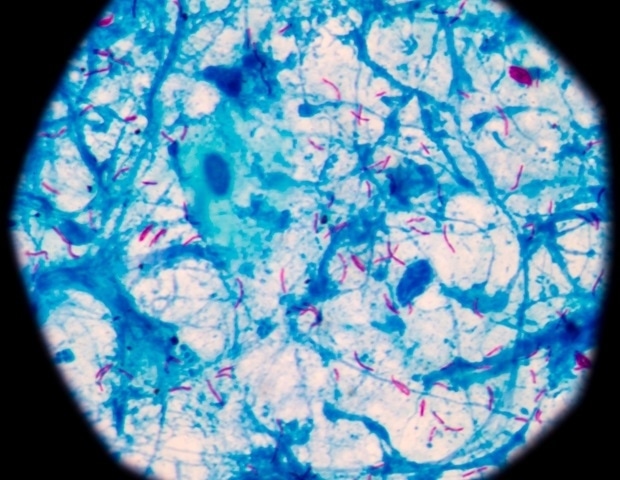
Tuberculosis, or TB, is an airborne lung illness brought on by a bacterium known as Mycobacterium tuberculosis. After coming into the lung, these micro organism bury deep into the tissue and start to unfold, inflicting the physique to launch an immune response and construct up clumps of immune cells surrounding the micro organism, known as granulomas, in an effort to manage the an infection and decrease injury to the lungs.
The immune response over the course of tuberculosis an infection has two phases. The primary six weeks after the an infection are characterised by the inflow of quick-acting immune cells that rush to the positioning of an infection, be that the airways or the lung, to kill the bug and restrict the injury rapidly, by all means mandatory. In contrast to the early innate immune response, the adaptive immune response that emerges after eight to 10 weeks of an infection is extra fine-tuned and aimed toward exactly concentrating on the precise infection-causing pathogen and killing it as effectively as doable. Typically, although, the precise dynamics of the immune response in tuberculosis, and the position of fast-acting CD8+ lymphocytes was unclear.
Flynn and her group discovered that the an infection was growing rather a lot sooner and spreading additional in macaque monkeys whose innate CD8+ cells had been depleted than in monkeys whose complete CD8+ T cell inhabitants was intact, or whose adaptive CD8+ T cells had been eliminated, suggesting that innate CD8+ cells play an important position in limiting the an infection in its early phases.
Utilizing a way known as bacterium barcoding, researchers tracked the lineages of bacterial granulomas that fashioned over the course of the illness. In animals missing innate CD8+ cells, researchers recognized extra bacterial dissemination throughout lungs and lymph nodes, suggesting that innate CD8+ cells create a “bottleneck,” stopping micro organism from establishing energetic an infection.
Curiously, researchers discovered that in monkeys with depleted innate CD8+ cells, different immune cells tried to take over the perform of quick responders, in all probability in response to IL-15. However as a result of these cells lack the pure equipment that might allow them to ship molecules that might kill the bacterium, the infection-clearing immune response was incomplete.
As a subsequent step of their analysis, scientists are learning whether or not IL-15 administered along with an present TB vaccine can enhance safety and make the vaccine simpler.
This examine was a collaboration between Flynn’s lab and Philana Ling Lin, M.D., of UPMC Kids’s Hospital of Pittsburgh, Dr. Alex Shalek, Ph.D., of the Massachusetts Institute of Know-how, and Sarah Fortune, M.D., of Harvard College.
This analysis was funded by Nationwide Institutes of Well being grants R56 AI139053, K12 HL143886 and 75N93019C00071, the Invoice and Melinda Gates Basis, Harvard College Middle for AIDS Analysis (P30 AI060354) and the Harvard Medical and Translational Science Middle (KL2 TR002542).
Supply:
Journal reference:
Winchell, C, G., et al. (2023) CD8+ lymphocytes are essential for early management of tuberculosis in macaques. Journal of Experimental Drugs. doi.org/10.1084/jem.20230707.