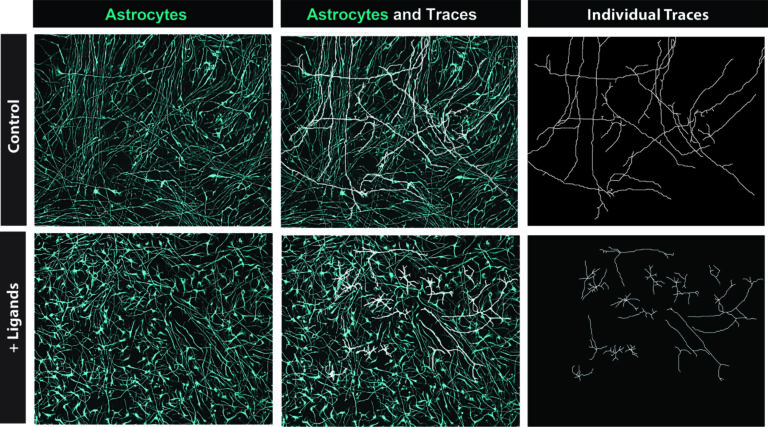
Astrocytes are a kind of glial cell within the central nervous system that clear extra neurotransmitters, promote the formation of synapses (i.e., connections between neurons), and carry out different capabilities. The event of astrocytes, like that of different glial cells, is partly supported by extrinsic ligands. Ligands are molecules that bind to a receiving protein, often known as a receptor, eliciting numerous mobile responses.
Researchers at Emory College College of Drugs just lately got down to establish ligand-receptor pairs that assist the genesis and improvement of astrocytes within the human mind utilizing computational methods. Their paper, revealed in Nature Neuroscience, highlights the potential of analyzing giant quantities of obtainable knowledge to establish new neuroscientific hypotheses.
“This work was initially impressed by our have to pivot our lab efforts with the onset of the COVID pandemic,” Steven A. Sloan, one of many researchers who carried out the examine, instructed Medical Xpress. “We now have a longstanding curiosity in how the fates of neurons and astrocytes are determined throughout early mind improvement. It is outstanding, as a result of these cell sorts share the identical progenitors, however these progenitors utterly swap their destiny from making neurons to astrocytes throughout a particular developmental time window.”
The “gliogenic swap” by which progenitor cells in the end produce astrocytes has been investigated for many years. Previous research on this space uncovered a number of molecular adjustments and secreted molecules that may underpin this swap, in the end altering the destiny of progenitor cells.
“We figured there absolutely have to be extra molecular adjustments that have not been recognized but,” Sloan defined. “Most of research on this space occurred over a decade in the past, and since then there was an explosion of genomic knowledge and significantly single cell sequencing of the fetal mind. So, once we weren’t capable of get into the lab to do experiments throughout COVID, we thought we might mine these datasets and work out what molecules could be signaling to one another within the creating mind to assist swap progenitors fates away from neurogenesis and in direction of astrogenesis.”
The current work by Sloan and his colleagues was impressed by a earlier paper revealed in Nature Strategies, which launched an algorithm to research organic and genomics knowledge. This advanced algorithm, referred to as NicheNet, had to date been used to handle different analysis questions that didn’t relate to the event of astrocytes.
“NicheNet is a sophisticated algorithm that has a comparatively easy clarification,” Sloan mentioned. “Computationally, we first needed to enter RNA-seq (single cell) knowledge of cells that we hypothesized could be sending a sign. In our case, these had been the cells within the mind which might be current earlier than astrogenesis (largely, immature neurons). Subsequent, we needed to outline the cells that could be receiving the alerts (progenitors referred to as radial glia).”
After the researchers fed the algorithm related RNA-seq knowledge and outlined cells that could possibly be receiving alerts from them, NicheNet analyzed the information. Basically, it tried to match molecules with receptors, figuring out molecules may need been secreted by sender cells that bind to receptors expressed on receiver cells. This evaluation produced an inventory of attainable ligand-receptor pairs concerned within the genesis of astrocytes.
“We then took this one step additional: as an alternative of simply selecting a few of these candidates, we might filter them by their predicted capability to activate astrocyte genes,” Sloan defined. “This helped loads, vastly narrowing down our nominated checklist of candidate molecules. There have been some in that checklist we acknowledged from the literature, and others that had been utterly new to us. We thought we might attempt to discover a small cocktail of ligands that may act complementary to one another, with the concept these molecules in all probability do not act in isolation.”
From the output produced by the NicheNet algorithm, the researchers recognized 5 ligands, every of which might activate a unique set of astrocytes genes. Notably, the genes activated by every of those ligands wouldn’t overlap with one another.
Sloan and his colleagues added these 5 ligands to organoids (i.e., simplified variations of organs created in laboratory settings) that they had been rising of their lab. After 30 days, they utilized RNA-sequencing to the organoids to find out if the ligands had influenced the destiny of progenitor cells, selling the genesis of astrocytes.
“We noticed a profound upregulation of astrocyte genes and downregulation of neuronal genes,” Sloan mentioned. “It actually appeared that the ligands had been shifting cell destiny! We repeated this experiment at a number of timepoints to see when the ligands exert essentially the most impact, and it appears they do that because the receptors enhance in expression nearer and nearer to the gliogenic swap. We additionally in contrast including all 5 ligands to including every ligand one-by-one and noticed that the cocktail was stronger in inducing this astrocyte dedication.”
The researchers carried out some further experiments to validate the results they noticed within the organoids. Particularly, they launched the 5 ligands they recognized in human cells and noticed what occurred.
“Lastly, we tried to slim down which molecular pathways these ligands had been activating to push progenitors in direction of an astrocyte destiny,” Sloan mentioned. “We queried an assortment of frequent signaling pathways with a mini-screen and located numerous adjustments. But one which stood out to us was a pathway referred to as mTORC1, which had been beforehand implicated in astrocyte biology. Subsequently, we additional validated activation of this pathway upon ligand stimulation and nominate it as a putative regulator of astrocyte improvement in people.”
By analyzing present datasets utilizing the NicheNet algorithm, Sloan and his colleagues had been capable of delineate a speculation that they then examined of their lab. Their paper thus reiterates the massive potential of computational strategies for conducting analysis in neuroscience.
“Analysis teams are persevering with to pour out increasingly more giant knowledge with the hopes that they’re going to result in new testable hypotheses and experiments,” Sloan mentioned. “Right here, we’re truly following by on that promise. Our examine identifies novel gliogenic ligands, however actually its greater image software is the truth that others might use these similar datasets to ask a whole lot of different questions on how cell-cell communication shapes early mind improvement.”
Future research might discover the attainable function of the ligand-receptor pairs recognized by this group of researchers within the additional improvement of astrocytes. As well as, this current paper might encourage the usage of NicheNet or comparable algorithms to sort out different analysis questions associated to neuroimmunology, myelination, neuronal specification, the diseased mind and different important neuroscientific subjects.
“Our current examine largely targeted on the extrinsic cues that affect astrocyte improvement,” Sloan added. “Sooner or later, we’re keen to raised perceive the intrinsic mobile alerts and states that permit a radial glia progenitor to transition from neurogenic to gliogenic fates. This swap appears to be implicated and disrupted in practically all neurodevelopmental issues, so a greater understanding of the mechanisms that govern this destiny choice is sort of necessary.”
Extra info:
Anna J. Voss et al, Identification of ligand–receptor pairs that drive human astrocyte improvement, Nature Neuroscience (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01375-8
5 molecules work collectively to drive human astrocyte improvement, Nature Neuroscience (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01391-8
© 2023 Science X Community
Quotation:
Examine identifies ligand-receptor pairs driving the event of astrocytes (2023, July 31)
retrieved 31 July 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-07-ligand-receptor-pairs-astrocytes.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.