Within the rush to harness synthetic intelligence and machine studying instruments to make care extra environment friendly at hospitals nationwide, a brand new examine factors to a different potential use: figuring out sufferers with non-medical wants that might have an effect on their well being and skill to obtain care.
These social determinants of well being—all the pieces from transportation and housing to meals provide and availability of household and buddies as helps—can play a significant function in a affected person’s well being and use of well being care companies.
The brand new examine focuses on a affected person inhabitants with particularly advanced wants: individuals with Alzheimer’s illness or different types of dementia. Their situation could make them particularly reliant on others to get them to medical appointments and social actions, deal with drugs and funds, store and put together meals, and extra.
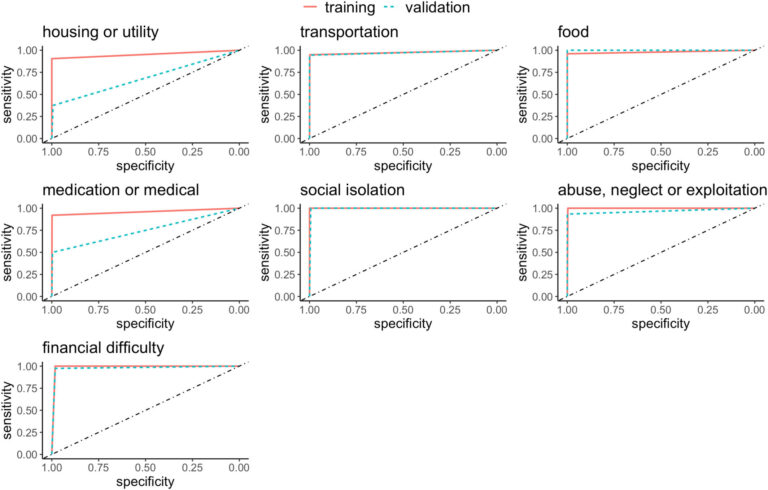
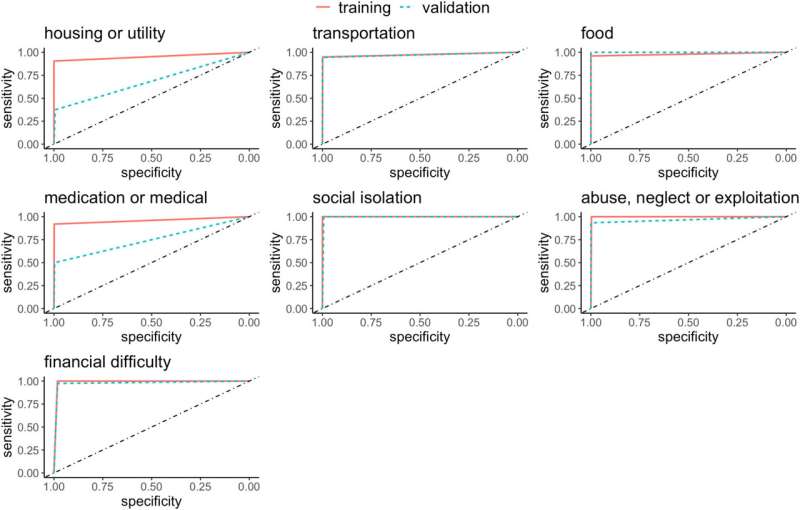
The outcomes of the examine present {that a} rule-based pure language processing device efficiently recognized sufferers with unstable entry to transportation, meals insecurity, social isolation, monetary issues and indicators of abuse, neglect, or exploitation.
The researchers discovered {that a} rule-based NLP device—a sort of AI that analyzes human speech or writing—was far superior to deep studying and regularized logistic regression algorithms for figuring out sufferers’ social determinants of well being.
Nevertheless, even the NLP device didn’t do properly sufficient at figuring out wants associated to housing or affording or taking remedy.
The examine was led by Elham Mahmoudi, Ph.D., a well being economist at Michigan Medication, the College of Michigan’s tutorial medical heart, and Wenbo Wu, Ph.D., who accomplished the work whereas incomes a doctorate on the U-M College of Public Well being and is now at New York College. Mahmoudi and two different authors are within the Division of Household Medication.
They and their colleagues in contrast the SDOH-spotting capabilities of three totally different AI strategies, first coaching them on a set of 700 affected person information to show them the sorts of phrases and phrases to search for, after which utilizing them on 300 information and judging the outcomes.
The instruments solely seemed on the anonymized contents of emergency division and inpatient social employee notes made between 2015 and 2019 within the digital well being information of 231 sufferers with dementia.
Mahmoudi says the crew is now working to prospectively validate the NLP algorithm in opposition to the SDOH questionnaire that has not too long ago begun to be supplied to all major care sufferers at Michigan Medication. That can enable them to check what the pc program finds and what sufferers say in response to questions on their scenario.
“We’re additionally getting ready a pilot program that can consider the feasibility of an intervention that addresses these social determinants of well being, and join recognized individuals with group assets,” mentioned Mahmoudi. “Within the meantime, we hope our present outcomes present that this algorithm can be utilized by clinicians, case managers and social staff to proactively handle the social wants of sufferers with dementia, and doubtlessly different weak affected person populations.”
Along with Mahmoudi and Wu, the examine’s authors are Kaes J. Holkeboer and Lorrie Carbone LMSW of the U-M Division of Household Medication, and Temidun O. Kolawole of Johns Hopkins College.
Extra info:
Wenbo Wu et al, Pure language processing to establish social determinants of well being in Alzheimer’s illness and associated dementia from digital well being information, Well being Companies Analysis (2023). DOI: 10.1111/1475-6773.14210
Quotation:
Can AI assist hospitals spot sufferers in want of additional non-medical help? (2023, August 14)
retrieved 14 August 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-08-ai-hospitals-patients-extra-non-medical.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.