Might music have an effect on cells? In keeping with a latest life science venture, it’s attainable. The outcomes could also be a primary step to utilizing music to deal with diabetes.
You probably have diabetes, the cells within the pancreas are unable to provide insulin, which is required by the physique to manage blood sugar. At the moment, efforts are being made in labs worldwide to create insulin-producing cells from human induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (hiPSCs) that may change insulin dietary supplements.
Considered one of these analysis environments was the ABINO venture, the place biologists, physicists and music expertise researchers have labored collectively to enter the sphere from a special approach: influencing cells by way of music.
Researcher Dongho Kwak virtually needed to begin from scratch when he started his Ph.D. as a part of the venture. He had a background in audio expertise and, as an orchestral flutist; he knew that sound can have an effect on the physique to some extent. Nevertheless, aiming to analyze the mobile degree, he didn’t have a lot different analysis to take a look at.
There had been some former makes an attempt to stimulate cells with sound, however there was an absence of systematic analysis.
Rhythms are important in biology
“I used to be curious as as to if I might form a sound related to dwelling cells. The truth that cells can sense sound in any respect was not apparent,” Kwak says, a analysis fellow on the RITMO Heart for Interdisciplinary Research in Rhythm, Time and Movement on the College of Oslo.
He needed to work systematically, he explains.
“Mainly, you’ll be able to take any piece of music and play it for the cells within the lab. Nevertheless, the evaluation will get a bit troublesome. Music has complicated buildings; it has many alternative parts, corresponding to melody, concord, and rhythm. It may be troublesome to say exactly what impacts the cells.”
Whereas serious about what a key component may very well be, analysis in physiological methods grabbed Kwak’s consideration. In “Rhythms in Physiological Methods” from 1991, he discovered an fascinating assertion within the introduction: “Rhythms are a fundamental phenomenon in all physiological methods.”
“The authors illustrated that rhythm has a elementary operate in crucial elements of the physiology, corresponding to cardiovascular, respiratory, and motor methods. For music, it’s the identical, as a result of, what’s music with out rhythm?”
Sound affected the cells
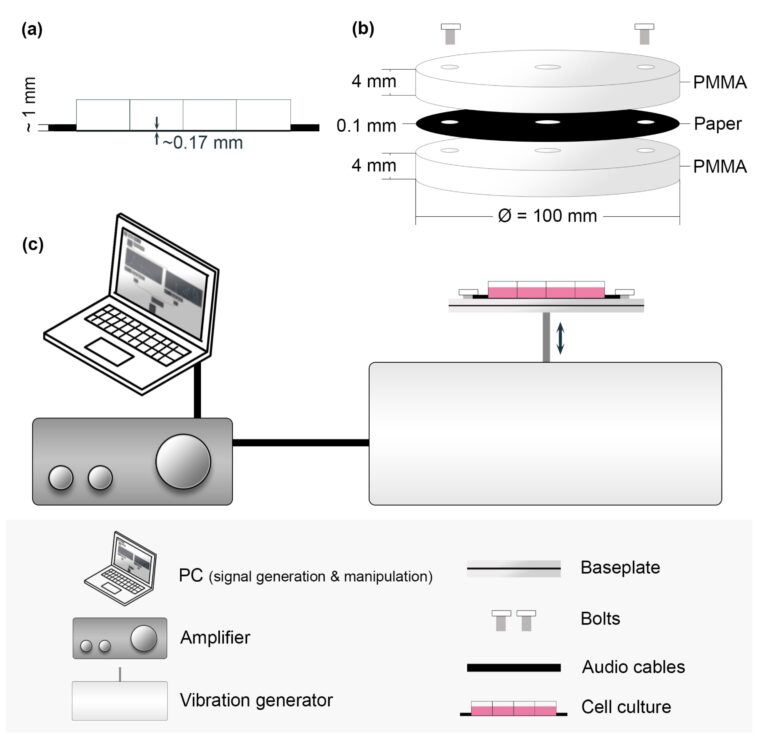
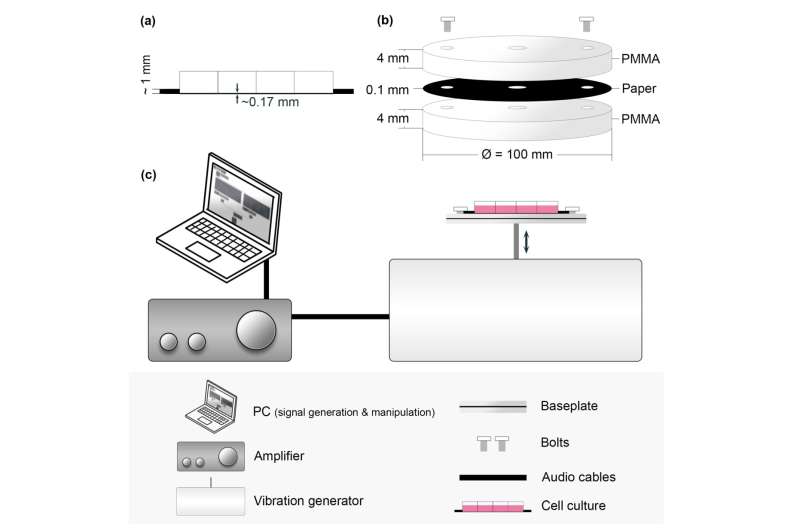
Kwak divided the cells into 4 teams: One group was uncovered to a gentle rhythm for fifteen minutes, the second to an irregular rhythm, the third to a steady sound, and the fourth was a management group with no sound.
Afterwards, he studied the cells’ filaments. These are skeleton-like buildings within the cells partly made from skinny, lengthy threads, and they’re delicate to exterior influences.
“In our revealed work, now we have preliminarily concluded that the filament buildings have shrunk after being uncovered to sound. They’d change into shorter. The impact was strongest for the cells that had been uncovered to a steady sound. Maybe the continual sound was inflicting essentially the most stress.”
The outcomes are revealed within the journal Bioengineering. Kwak describes them as a milestone, however prefers the phrase “preliminary” because of the uncertainty of the findings. Extra analysis is required to determine a safe hyperlink between rhythm and cell conduct, he explains.
The examine could open new methods to experiment with cells
The modifications we noticed within the sound-exposed cells don’t indicate that music is nice or dangerous for cells, Kwak emphasizes.
“It solely means that cells reply to rhythmic sounds in an fascinating means, which supplies researchers one thing to work on. It may very well be that cells would reply to totally different pitches and ranging intensities as effectively, however we have no idea that but.”
Professor Alexander Refsum Jensenius is the pinnacle of the RITMO middle and one of many initiators of the analysis venture Kwak has been engaged on.
“The truth that rhythmic sound appears to have an effect on the cells is extremely fascinating. Normally, cell researchers want loads of chemical compounds to stimulate cells. Whether it is attainable to stimulate cells utilizing vibration, corresponding to sound, it might result in new methods of experimenting with cells,” Jensenius says.
A necessity for sturdy protocols
The thought behind the ABINO venture got here throughout when Jensenius was sitting subsequent to cell researcher Hanne Scholz at a dinner. Scholz had heard lab individuals speak about music within the lab seemingly affecting cells. Scholz, a researcher on the School of Medication, College of Oslo, was the venture chief of ABINO.
The workforce hopes that the venture will encourage additional analysis on this route to grasp how cells would reply to rhythms.
Creating insulin-producing cells, which may very well be transferrable to people as stem cells, continues to be an extended shot, in keeping with Jensenius.
“Nevertheless, if we’re to get there, we’d like sturdy protocols, which means strategies. Discovering new methods of cultivating cells within the lab is unquestionably of curiosity,” Alexander Refsum Jensenius says.
Extra data:
Dongho Kwak et al, Characterization of Mechanical and Mobile Results of Rhythmic Vertical Vibrations on Adherent Cell Cultures, Bioengineering (2023). DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering10070811
Quotation:
Analysis investigates music’s results on cells with implications for diabetes remedy (2023, November 17)
retrieved 17 November 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-11-music-effects-cells-implications-diabetes.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.