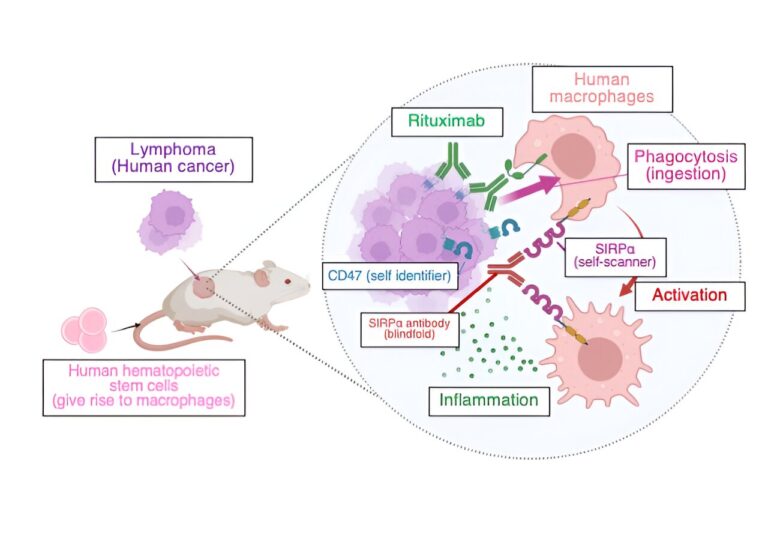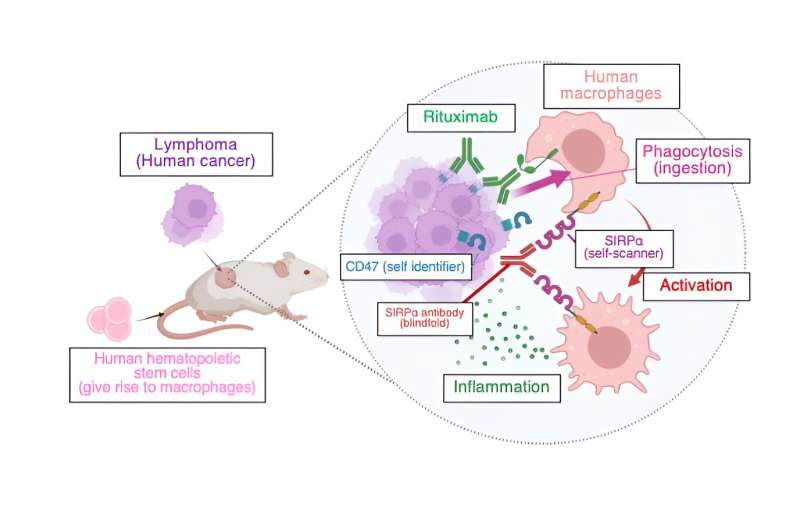
Mice with human immune cells are a brand new means of testing anti-cancer medicine focusing on the immune system in pre-clinical research. Utilizing their new mannequin, a Kobe College analysis staff efficiently examined a brand new therapeutic strategy that blindfolds immune cells to the physique’s self-recognition system and so makes them assault tumor cells.
Most cancers cells show constructions on their floor that determine them as a part of the self, and thus stop them from being ingested by macrophages, a kind of immune cell. Most cancers immunotherapy goals at disrupting these recognition programs.
Earlier research have proven {that a} substance that blinds macrophages to one among these identifiers, known as CD47, by disabling their CD47-scanning construction often called SIRPα, can activate the cells to struggle the tumor when given together with therapeutic cancer-targeting antibodies corresponding to Rituximab. Nevertheless, as a result of this strategy is so particular to the self-identification of human cells, till now it may solely be examined in people or monkeys, making pre-clinical research in mice inconceivable.
To beat this, Kobe College immuno-oncologist Saito Yasuyuki and his staff constructed on their expertise with creating mouse immunological fashions and transplanted components of the human immune system into mice.
He says, “Research utilizing mouse fashions with humanized immune programs have targeted on lymphocytes, a kind of immune cell related to infectious illnesses. The particular side of our strategy is that our new mouse mannequin focuses on macrophages as a result of we need to goal them for the event of recent most cancers immunotherapies.”
This enabled the researchers to each create a extra totally functioning mouse mannequin of human most cancers and take a look at the effectiveness of the blindfolding strategy for the primary time on this atmosphere.
Their outcomes, printed within the journal Frontiers in Immunology, confirmed that the macrophage-targeted remedy certainly induced an efficient most cancers response. Nevertheless, Saito explains, “Probably the most thrilling side of this result’s that this strategy not solely promotes the engulfment (ingestion) of tumor cells by macrophages but in addition reprograms tumor-associated macrophages, one of many present subjects of most cancers immunotherapy.”
The immune system has an ambiguous position within the growth of and struggle towards most cancers. On the one hand, it may acknowledge most cancers cells and struggle them. Alternatively, macrophages additionally affiliate with tumors, each supporting their progress and suppressing different anti-tumor immune responses. To show these cells towards most cancers is the novel strategy that the Kobe College researchers may now assist propel ahead with their new humanized mouse mannequin.
However the end result has a broader relevance, too. Saito says, “There have been no appropriate preclinical in vivo fashions to develop therapeutics focusing on human macrophages surrounding tumors, so new approaches needed to be examined straight on sufferers. I imagine our mannequin completely fills the hole and should assist in the choice of the best remedy from a number of candidates for therapeutics focusing on human immune cells. The long-term objective of my undertaking is to develop a humanized immune system mouse mannequin that faithfully represents the immune response towards the tumor.”
Extra info:
Preclinical analysis of the efficacy of an antibody to human SIRPα for most cancers immunotherapy in humanized mouse fashions, Frontiers in Immunology (2023). DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1294814
Quotation:
Utilizing mice with humanized immune programs to check most cancers immunotherapies (2023, December 14)
retrieved 14 December 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-12-mice-humanized-immune-cancer-immunotherapies.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.