A research revealed within the journal Alzheimer’s Analysis & Remedy describes that the Mediterranean and MIND diets might successfully protect episodic and visuospatial working reminiscence in midlife.
 Research: Food plan patterns and cognitive efficiency in a UK Feminine Twin Registry (TwinsUK). Picture Credit score: DiViArt / Shutterstock
Research: Food plan patterns and cognitive efficiency in a UK Feminine Twin Registry (TwinsUK). Picture Credit score: DiViArt / Shutterstock
Background
Age-related cognitive decline is a public well being concern as it might have an effect on morbidity and mortality. Though most people expertise cognitive decline in midlife, the speed of cognitive decline can considerably range between people relying on their cardiovascular well being and way of life behaviors. A faster-than-usual charge of cognitive decline with age could be a threat issue for Alzheimer’s illness.
Nutrient-rich dietary patterns, such because the Mediterranean (MED) and the Mediterranean-dietary approaches to cease hypertension intervention for neurodegenerative delay (MIND) diets, are identified to have neuroprotective and cognition-enhancing talents. On this context, proof signifies that the MED food plan can enhance cognitive capabilities by positively influencing the intestine microbiota.
On this research, scientists have investigated the impression of MED and MIND diets on cognitive operate and 10-year change in cognitive efficiency in cognitively wholesome feminine twins.
Research design
The research analyzed information obtained from the UK Grownup Twin Registry that enrolled wholesome feminine twins between 1992 and 2004. A complete of 509 feminine twins who had full baseline information on food plan and cognitive efficiency between 1998 and 2000 had been included within the evaluation. Of those twins, 34% had been monozygotic (genetically similar) and 66% had been dizygotic (50% similar genes).
The baseline dietary consumption was assessed utilizing a meals frequency questionnaire. The dietary consumption information was used to calculate food plan scores for the MED and MIND dietary patterns. A better dietary rating is indicative of upper adherence to the respective diets.
The individuals’ cognitive efficiency was assessed at baseline and after ten years (2008 – 2010). Six varieties of cognitive capabilities had been examined, together with response velocity, spatial working reminiscence, episodic reminiscence, visible episodic reminiscence, resolution time, and visuospatial working reminiscence.
Fecal samples had been collected from the individuals on the 10-year follow-up to research intestine microbiota.
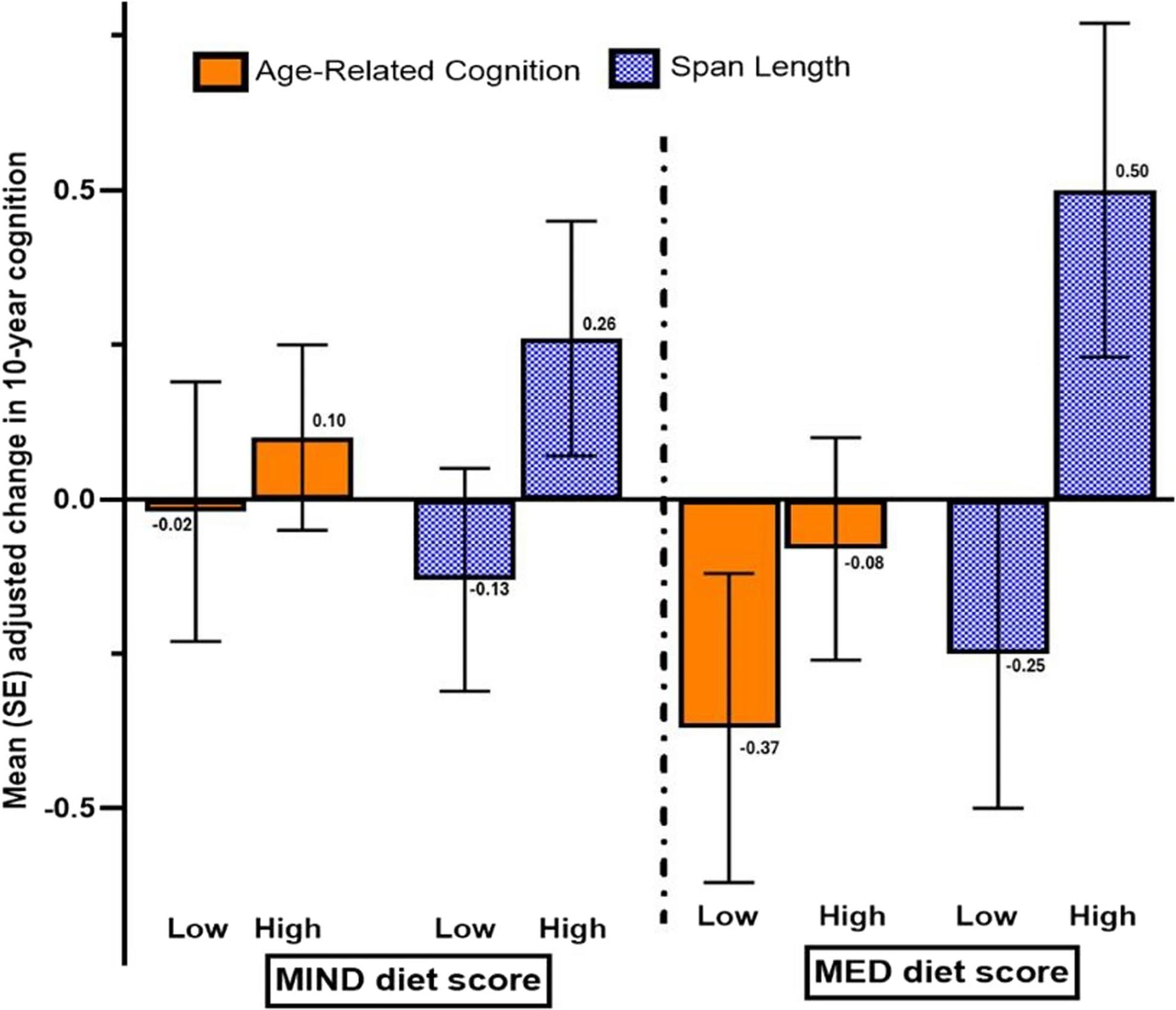 Change in adjusted imply (SE). Age-related cognition and spatial span size over 10 years in MZ twins discordant for MIND and MED food plan rating
Change in adjusted imply (SE). Age-related cognition and spatial span size over 10 years in MZ twins discordant for MIND and MED food plan rating
Vital observations
The evaluation of the impression of dietary patterns on baseline cognitive efficiency revealed no important affiliation between MED food plan scores and cognitive check scores. For the MIND food plan, every 1-point enhance in food plan rating was discovered to be related to quicker response time and higher visible episodic reminiscence after adjusting for demographic, well being, and way of life confounding components.
The evaluation of the impression of dietary patterns on cognitive efficiency at a 10-year follow-up revealed that growing adherence to the MED or MIND food plan is related to improved episodic reminiscence.
The evaluation of the impression of dietary patterns on 10-year change in cognitive efficiency within the discordant monozygotic twin pairs revealed that the monozygotic twin with a excessive food plan rating has much less decline in international cognition normally. Nevertheless, this distinction was not statistically important.
Inside every monozygotic pair, the dual with excessive MED or MIND food plan scores noticed larger preservation of visuospatial working reminiscence. This statement was important for the MED food plan. No important impression of MED or MIND food plan on 10-year change in different cognitive performances was noticed in discordant monozygotic twins.
Relating to the connection between dietary patterns and intestine microbiota, the findings revealed that top adherence to the MIND food plan at baseline is related to the next abundance of Ruminococcaceae UCG-010 (short-chain fatty acid-producing micro organism) and a decrease abundance of Dorea at 10-year follow-up. This affiliation turned non-significant after adjusting for dietary fiber consumption.
Additional evaluation revealed {that a} greater abundance of Ruminococcaceae UCG-010 is related to a decrease decline in international cognition and improved spatial working reminiscence on the 10-year follow-up.
Research significance
The research finds that each MED and MIND diets might successfully protect episodic and visuospatial working reminiscence in midlife. These neuroprotective results could possibly be attributed to excessive dietary fiber content material and elevated abundance of short-chain fatty acid-producing micro organism within the intestine.
As talked about by the scientists, the doable affect of unidentified genetic components on the research outcomes in the whole research inhabitants can’t be dominated out, as the identical sample of cognitive enchancment has not been present in monozygotic co-twins.
Future research ought to embody longer follow-ups with repeated cognitive assessments to know the impression of food plan on cognitive efficiency in older age.

