Human decision-making has been the main focus of a variety of analysis research. Collectively, these analysis efforts might assist to know higher how individuals make several types of on a regular basis decisions whereas additionally shedding mild on the neural processes underpinning these decisions.
Findings recommend that whereas making instantaneous selections, or in different phrases, decisions that should be made shortly based mostly on the data accessible at a given second, people significantly depend on contextual data. This contextual data can even information so-called sequential selections, which entails making a alternative after observing the sequential unfolding of a course of.
Researchers on the College of Oxford, the Nationwide Analysis Council in Rome, College Faculty London (UCL), and the Max Planck Institute for Human Improvement lately carried out a examine exploring the influence of context on goal-directed decision-making. Their findings, revealed in Neuron, recommend that goal-seeking ‘compresses’ spatial maps within the hippocampus and orbitofrontal cortices within the mind.
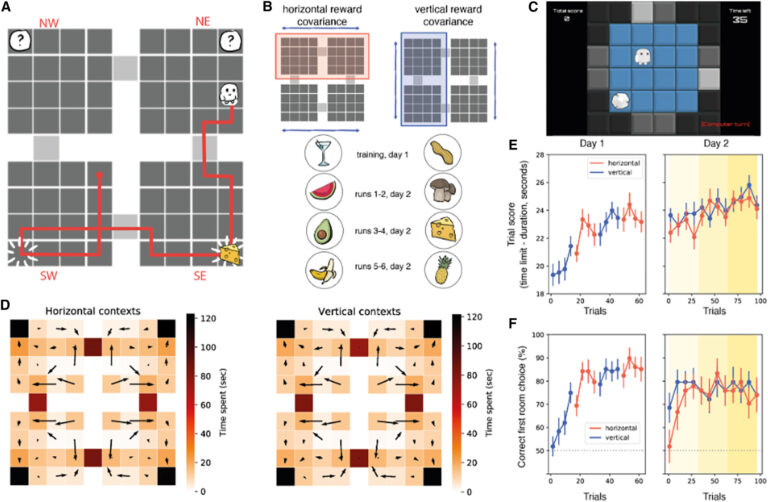
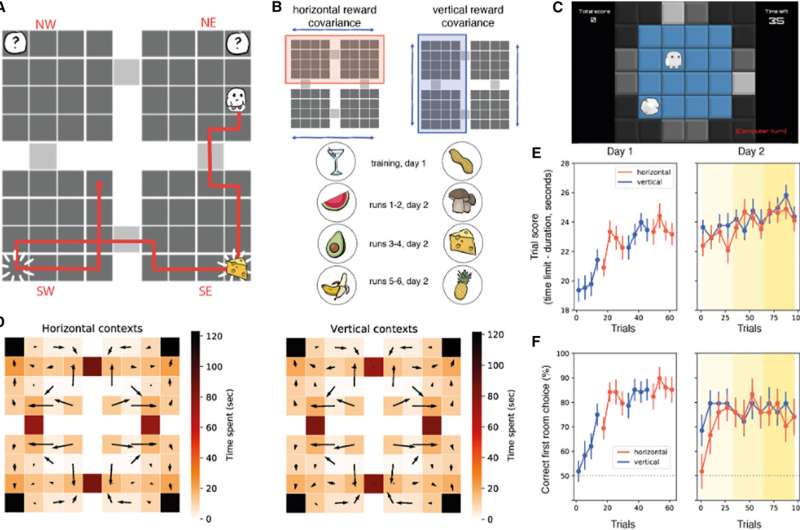
“People can navigate flexibly to satisfy their targets,” Paul S. Muhie-Karbe, Hannah Sheahan, and their colleagues wrote of their paper. “We requested how the neural illustration of allocentric area is distorted by goal-directed conduct. Individuals navigated an agent to 2 successive aim places in a grid world setting comprising 4 interlinked rooms, with a contextual cue indicating the conditional dependence of 1 aim location on one other.”
To additional discover what occurs within the mind throughout goal-directed decision-making, the researchers carried out an experiment involving 27 human contributors. These contributors accomplished a process on a pc display screen, which entailed navigating a digital setting by controlling an avatar.
This avatar might transfer by means of {a partially} seen world represented in a grid type. This digital world included 4 completely different rooms related to one another, and the contributors solely noticed the room that their avatar was occupying from above (i.e., with a chicken’s eye view).
Throughout every experimental trial, the contributors’ avatar appeared in a room picked at random, and the contributors had been requested to maneuver it utilizing buttons on a keyboard to choose up rewards by colliding with some boulders whereas avoiding boulders that had been empty.
At first of every trial, the contributors had been additionally supplied a contextual cue, which hid partial clues hinting (however not clearly disclosing) the place the rewards may very well be discovered inside the digital world. Notably, because the contributors accomplished this process requiring goal-directed decision-making, their mind exercise was recorded by an fMRI scanner.
“Inspecting the neural geometry by which room and context had been encoded in fMRI alerts, we discovered that map-like representations of the setting emerged in each hippocampus and neocortex,” Muhie-Karbe, Sheahan, and their colleagues wrote.
“Cognitive maps in hippocampus and orbitofrontal cortices had been compressed in order that places cued as targets had been coded collectively in neural state area, and these distortions predicted profitable studying. This impact was captured by a computational mannequin during which present and potential places are collectively encoded in a spot code, offering a concept of how targets warp the neural illustration of area in macroscopic neural alerts.”
Basically, Muhie-Karbe, Sheahan, and their colleagues discovered that the setting that was just about accessed by contributors was encoded within the type of a map in some elements of their brains, significantly the hippocampus and neocortex. Apparently, nonetheless, these cognitive maps had been considerably compressed, coding places that had been related to the aim they had been making an attempt to realize collectively.
These outcomes shed new mild on the neural underpinnings of goal-directed decision-making, suggesting that the mind might make the most of compression mechanisms to contextually modulate sensory data throughout decision-making to realize a selected aim. Sooner or later, new research might additional examine these compression processes, which might result in fascinating new discoveries.
Extra data:
Paul S. Muhle-Karbe et al, Objective-seeking compresses neural codes for area within the human hippocampus and orbitofrontal cortex, Neuron (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.08.021. www.sciencedirect.com/science/ … ii/S0896627323006323
© 2024 Science X Community
Quotation:
Cognitive maps in some mind areas are compressed throughout goal-seeking decision-making (2024, January 4)
retrieved 4 January 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-01-cognitive-brain-regions-compressed-goal.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.